

Chemistry higher tier
Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and
ribonucleic acid (RNA) are polymers.
These polymers have special significance in living cells as
they carry the genetic information
of the organism. Coded in the DNA is information used to control cell growth and development as
well as the information needed to carry out all the processes which keep the cell and ultimately
the organism alive. DNA is a molecule and like many large molecules it is a
polymer
build up from of many smaller units called monomers linked together. In the case of DNA the small
monomer units that
link together are called nucleotides.
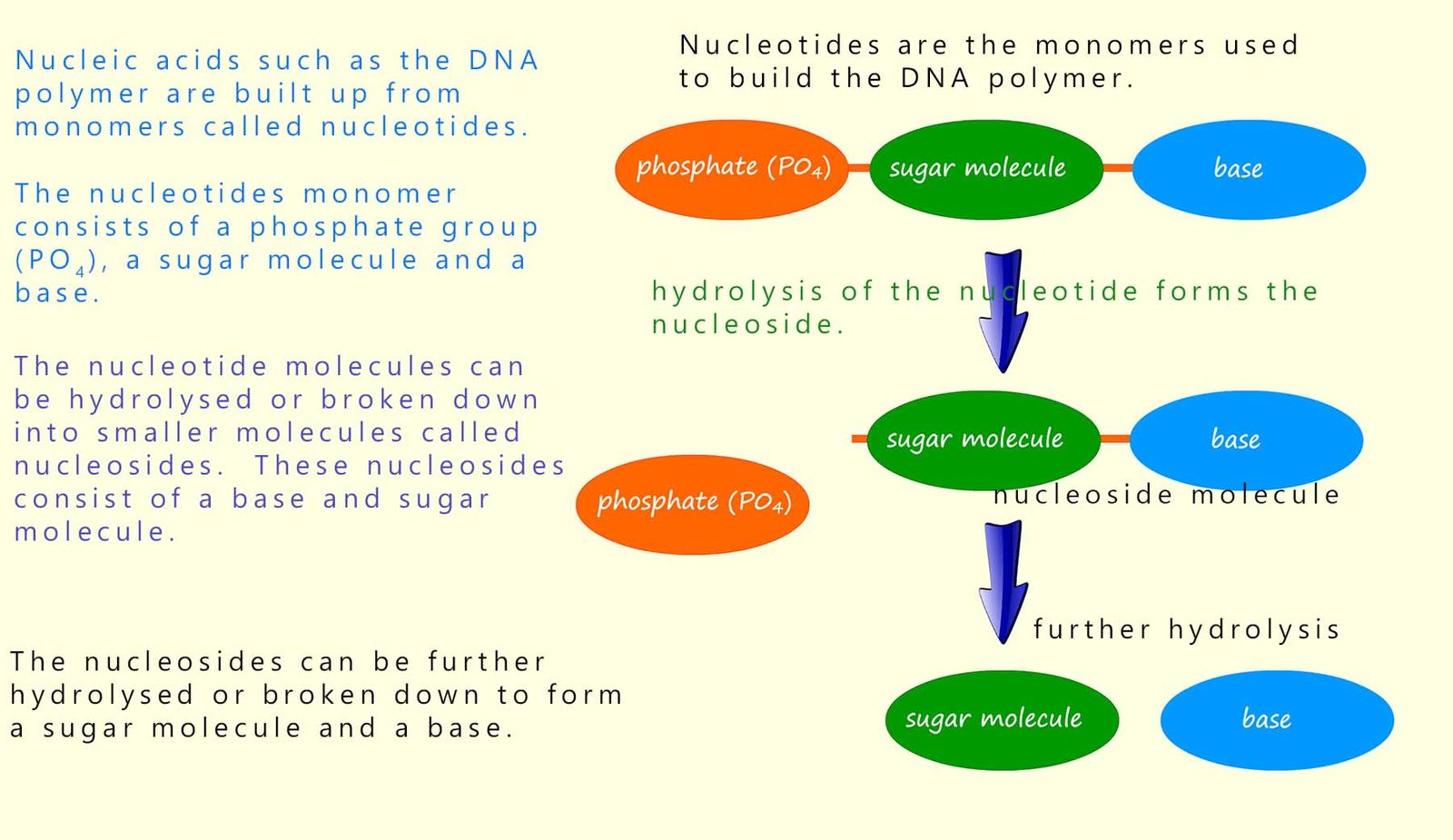
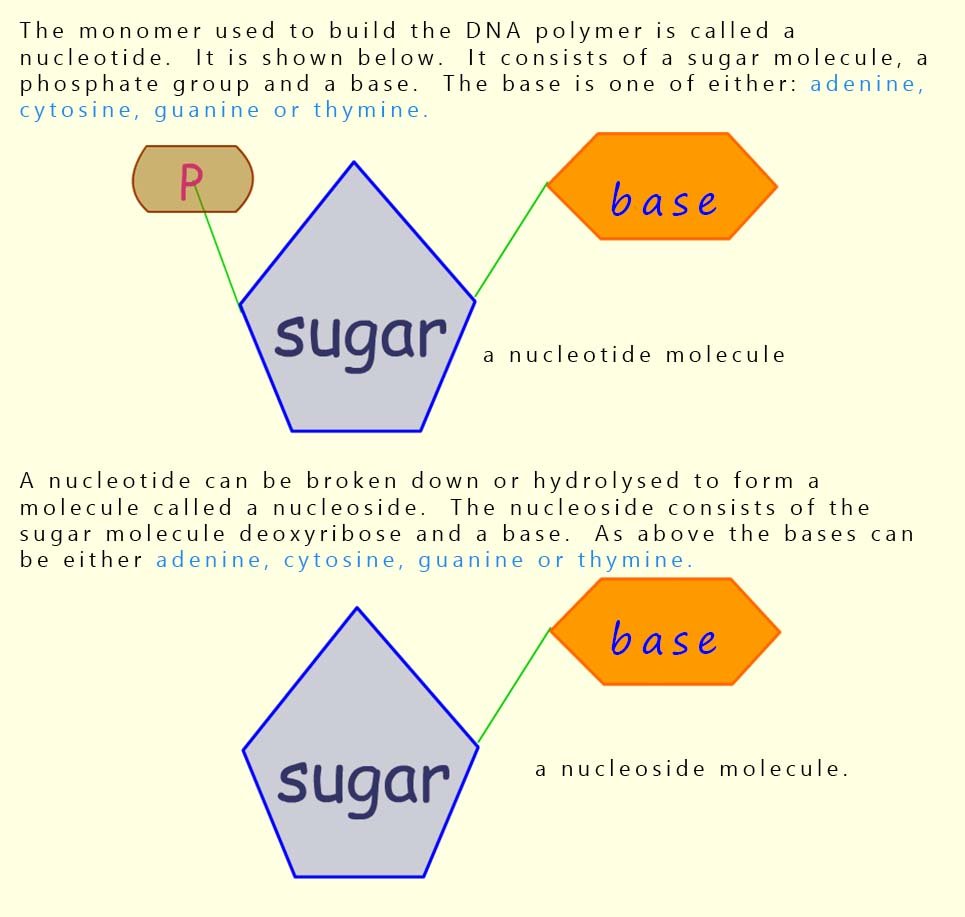
Nucleotides are the monomers from which the DNA
polymer is built. The nucleotides
consist of a base (sometimes called an amine base), a sugar molecule
and a phosphate group all linked together. An outline of the structure of the DNA polymer is shown below. The nucleotide monomers all contain the same sugar and phosphate group but there are four possible amine bases; so there are four different nucleotides.
Ribose is a simple sugar molecule that is made in the human body. Many people; mainly athletes take ribose supplements as it is claimed to give you extra energy and reduce fatigue. Its chemical formula is C5H10O4. Its structure is shown below.
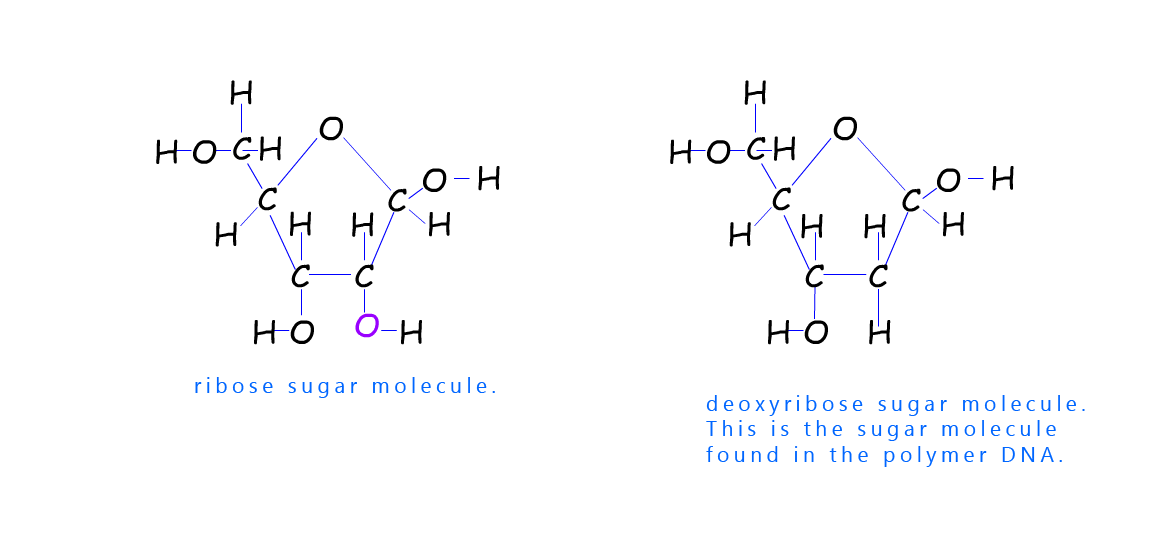
You can see that ribose sugar has a ring structure in the shape of a pentagon. Most of carbon atoms
in
the 5 membered ring are joined to a H atom and an O-H group. The second sugar molecule shown is
deoxyribose;
this is very similar to the structure of ribose sugar except there is one atom of oxygen
missing on the
second carbon atom in the ring (deoxy indicates that oxygen is missing). This sugar
deoxyribose is
the one found in DNA.
As mentioned above the monomers for the DNA polymer; the nucleotide molecules consist of a phosphate group (PO42-), a sugar (deoxyribose) and a base all linked together. The sugar molecule found in DNA is called deoxyribose and there are four different bases found in the nucleotides. These bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine. The names of these 4 bases are often simply shortened to the letters A, G, C and T.
The nucleotide molecules can be hydrolysed to give simpler
molecules called nucleoside. Nucleosides consist
only of a sugar molecule, deoxyribose and a base, one of
adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine, this is shown below:
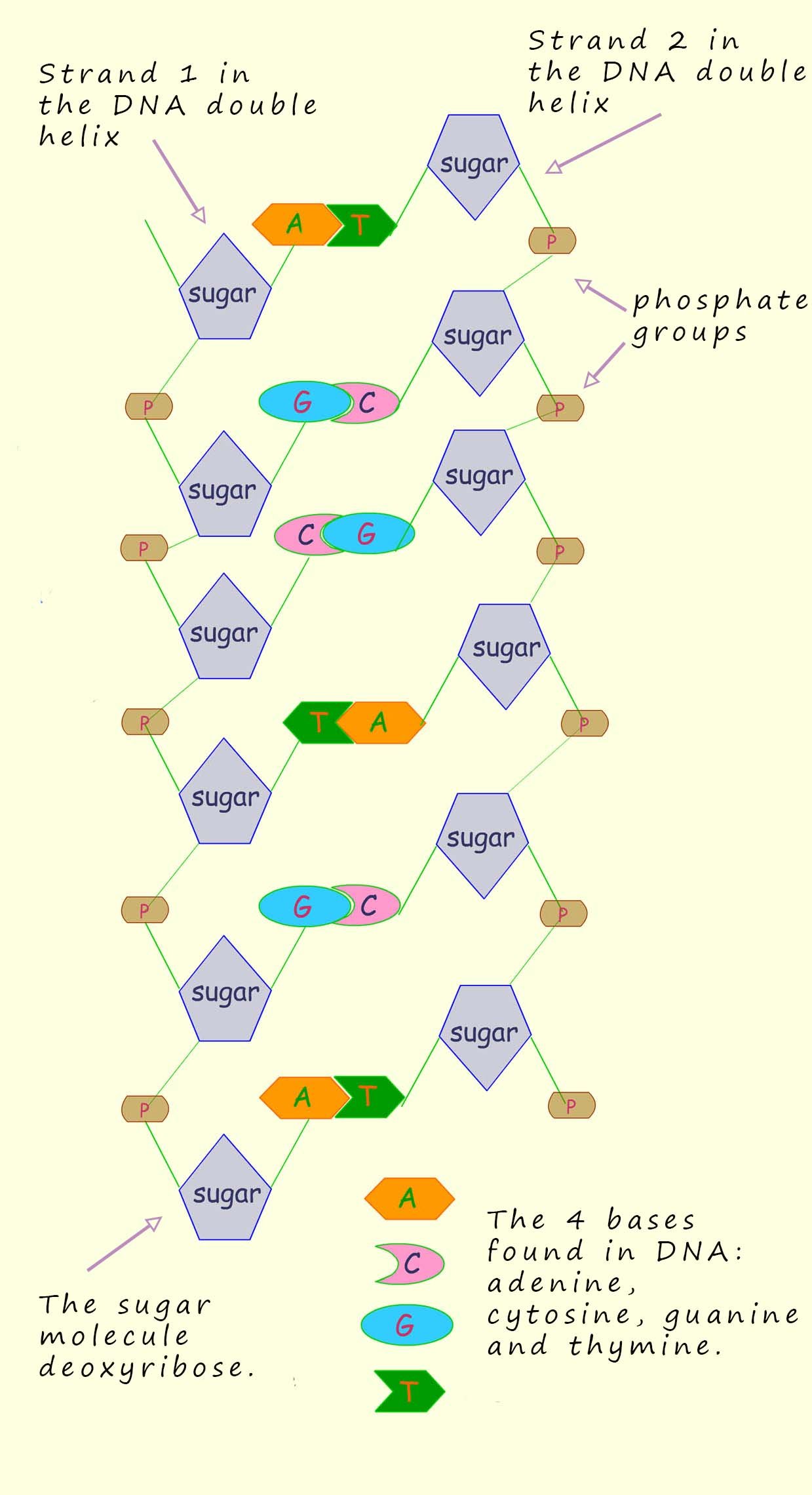
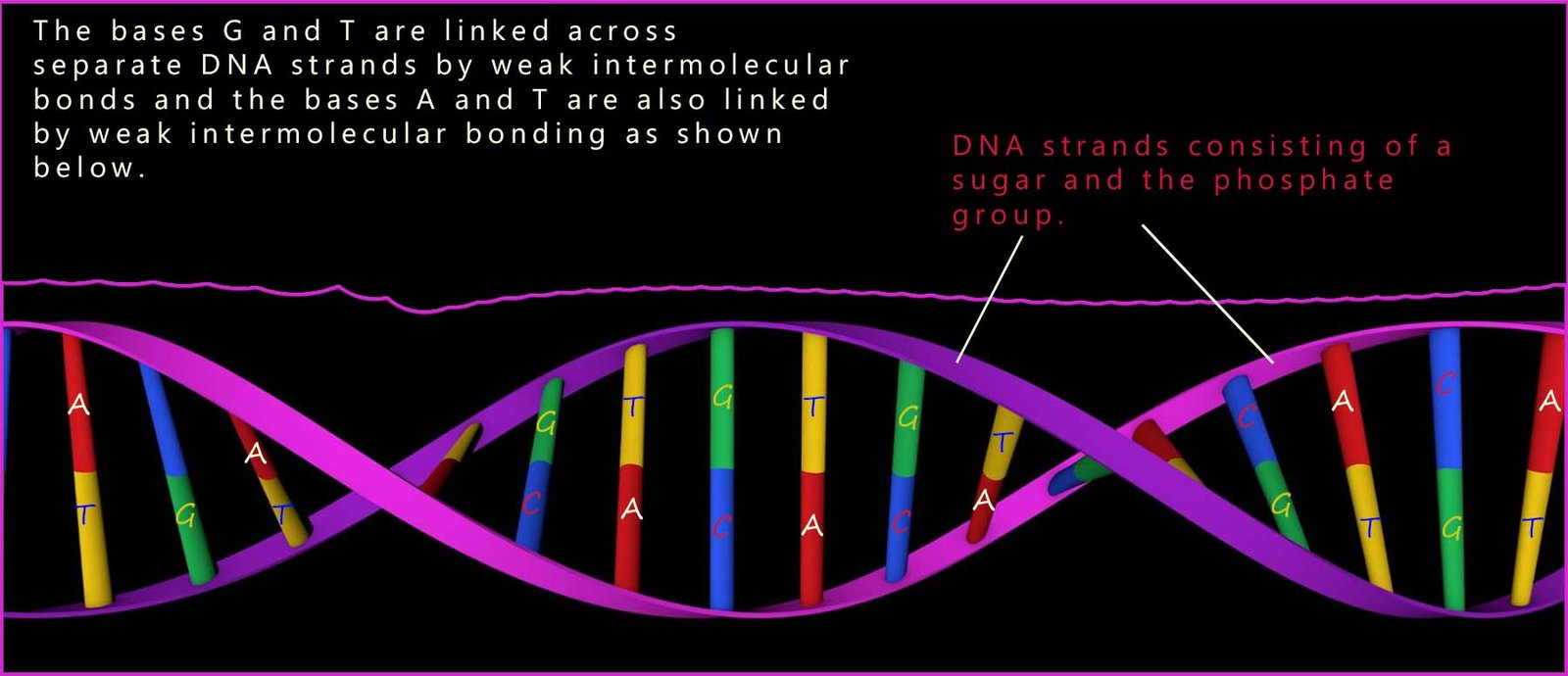
The structure of the DNA polymer resembles a coiled spring or to give its structure the proper name; it is referred to as a double helix (shown at the bottom of the page and in the image opposite). The phosphate groups and the sugar molecules form the long strands of the helix while the bases link together the two strands of DNA which make up the double helix. This gives the basic structure of DNA as shown where there is a backbone of phosphate-sugar molecules linked up with the bases sticking out from the sugar molecules.
Remember the bases are either one of four molecules: A,T,G or C. The order or sequence of these bases is different in different people and this is one of the factors that makes us all different from one and other.
Drag (or tap to select, then tap to place) the correct pieces into the slots to build one DNA nucleotide: phosphate + deoxyribose + DNA base.
In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick suggested the structure of DNA consisted of two of these
polymer strands shown opposite twisted together in a double helix structure. The two strands of
nucleotides run in opposite directions to each other.
The two strands are attracted to each other
through weak intermolecular bonding between the bases on each strand. However Watson and Crick
found that the intermolecular bonding between the two strands of DNA ONLY occurs between the bases adenine (A) and thymine (T) on different
strands and between guanine (G) and cytosine (C) bases on different strands. This is outlined in the image above.
The reason for this A......T and G.....C base pairing on different DNA strands is simply due
to the shapes of the base molecules which allows them to fit together easily and so allows
strong intermolecular attraction between the two DNA strands. The image below shows the
twisted double helix shape of the DNA molecule and the image on the side of the page shows the base pairings across the two strands of DNA in the double helix structure.
The strands consist of the phosphate- sugar molecules with the bases paired up across the strands.
Below is a short section of DNA strand 1. Build strand 2 (the complementary strand) using the buttons.
In DNA: A pairs with T, and G pairs with C.